2 dead, 58 sick from Harlem Legionnaires’ disease cluster – NBC New York

A second person has now died and more than 50 people have fallen ill as part of a growing Legionnaires’ cluster in Harlem, city health officials reported Monday.
The disease was initially detected on July 25; since then, two people have died and 58 people have been diagnosed, the New York City Health Department revealed in its latest update.
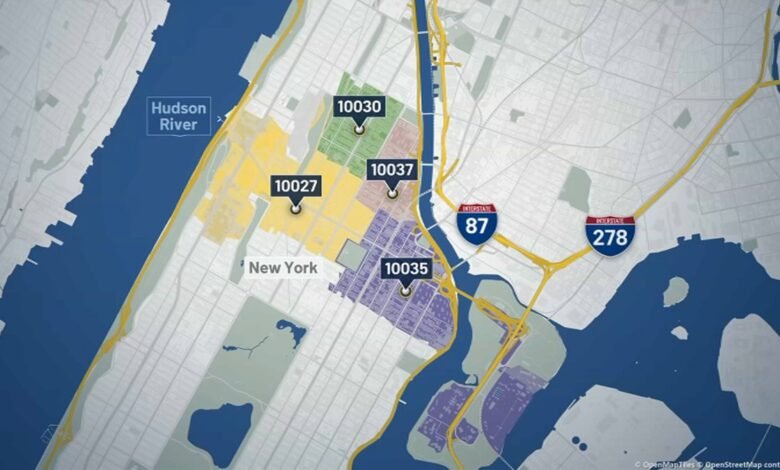
Legionnaire’s, a type of pneumonia, is caused by the bacteria Legionella, which grows in warm water. The cases from the cluster have been found in five Harlem ZIP codes: 10027, 10030, 10035, 10037 and 10039, along with the bordering communities, according to health officials.
“If you’re in those ZIP codes that have demonstrated exposure, then we want you to monitor your symptoms and get to a healthcare provider as soon as you can so you can get access to antibiotics, because it is treatable,” said Dr. Tony Eyssallenne, the deputy chief medical officer for the city’s Health Department.
All cooling towers that are operating in the impacted area have been sampled, and the Health Department has told owners of buildings where positive results were found to initiate remediation within a day.
Those who have been in the impacted area since late July and have been experiencing flu-like symptoms, fever, cough or difficulty breathing should seek medial attention immediately, according to the Health Department.
Legionnaires’ disease is not transmitted from person to person, and is treatable with antibiotics. It spread by breathing in water vapor containing the Legionella bacteria. Conditions for the bacteria to grow are favorable in things like cooling towers, whirlpool spas, hot tubs, humidifiers, hot water tanks and condensers of large air-conditioning systems.
An investigation is ongoing.
Individuals at higher risk include those 50 years old and older, cigarette smokers, and people with chronic lung disease or compromised immune systems. People living or working in the area who are experiencing these symptoms should seek medical attention with a primary care provider or seek urgent care, officials say.
In 2022, at least five people died of Legionnaires’ disease over the summer at a Manhattan nursing home in the city’s worst outbreak, in terms of total cases, since a cooling tower in the Bronx was blamed for an infection that caused 16 deaths. Usually, about 200 to 700 people are diagnosed each year, official health data show.
What is Legionnaires’ disease?
Legionnaires is a type of pneumonia, or a lung infection, the state DOH said.
The legionella bacteria can also lead to a milder illness called Pontiac fever, which resembles flu-like symptoms.
How does it spread?
Legionella bacteria spread when someone inhales tiny droplets of contaminated water, commonly found in hot tubs, industrial air conditioning systems, decorative fountains, plumbing systems and even drinking water.
Outbreaks often occur in large and complex water systems found in places like hotels, hospitals, and cruise ships.
The bacteria can also survive and spread in soil, occasionally causing infections when people garden using contaminated soil.
However, in most cases, people do not transmit Legionnaires’ disease or Pontiac fever to others.
What are the symptoms?
Symptoms of Legionnaires disease typically appear between two to 10 days after exposure to the bacteria and can include:
- Headache
- Muscle aches
- Shortness of breath
- Cough
- Fever
The New Jersey Department of Health noted that the symptoms can be similar to those of COVID-19 and other respiratory illnesses like the flu. Only tests ordered by a doctor can confirm a diagnosis.
Who is at higher risk?
Those most susceptible to Legionnaires’ disease include adults over 50, individuals with weakened immune systems or chronic conditions, and smokers.
It is rarer for healthy people who are exposed to the legionella bacteria to develop Legionnaires’ disease.
Can it be treated?
Antibiotics are used to treat Legionnaires’ disease, though it often requires hospitalization.
Anyone suspecting exposure to Legionella or experiencing symptoms of Legionella disease or pneumonia should promptly contact a doctor. It’s important to mention any exposure to Legionella, hot tub use, recent travels, or hospital stays in the past two weeks.
For more information on Legionnaires’ disease, visit the CDC website.






